(Last updated on November 2nd, 2022)
Adobe Photoshop is a pretty robust program, but how does it fare in 8-bit or 16-bit color modes? Which one is better to work with, and which one is more capable of your design needs? Find out in this comparison of the two different modes of color with their pros and cons.
Photoshop has become such an industry standard that many aspects have become second nature for the designers who have been using it for quite some time. Everything from merging layers to managing adjustments has become essential to use the program.
While Photoshop is capable of many projects, ranging from raster graphics to video assets, one does have to question which aspects of the program would benefit them both. After all, the last thing you want is a large image for an online graphic or RGB for a print job.
Related: How Much Does Photoshop Cost?
But there’s another aspect to Photoshop’s color modes that one may not consider as much: 8-bit versus 16-bit color modes. It seems like an aspect that isn’t questioned as much. One’s mind may even be drawn back to the 1990s console war with such talk about which video game system had the better graphics.
Photoshop 8 bit vs 16 bit: Are More Bits Better?
The knee-jerk response to which color mode is best would seem to be 16-bit, right? That’s more than 8-bits, and you want lots of detail for your project. But this subject is about more than just ensuring your design doesn’t turn out like an old-school Nintendo game.
There are a few pros to working in a 16-bit color mode. It’s better suitable if you intend to do a lot of color correction. So if you know you’re going to be working with images that require specific colors to pop or be toned down, you’ll find it easier to do when there are fewer data lost in this mode.
The other thing to consider is just what type of source files you’re working with. If the images you’re handling have a lot of color to them, a 16-bit environment will be able to read more colors and present them far better than that of 8-bit.
You also have the benefit of having more colors to work with in terms of gradients. The range that color can span in a gradient is limited within the 8-bit mode, but 16 bits grants a vaster array of transition to make the fall-off of colors more fluid and less distracting.
If you want to see a clear difference, simply look at any histogram of color or levels within Photoshop. Notice how in 8-bit mode the spikes are further apart and that in the 16-bit mode, they are closer together, appearing more like small waves than pointy fences.
This difference is due to how much more information is coming through with each mode. This difference may seem obvious given the aspects previously listed, but it can sometimes be beneficial to see just how the two modes differ in a more visually noticeable way.
Flaws of 16 Bit Mode
But there are also some drawbacks to going 16 bit. There’s a restriction in just what types of filters you can use in this color mode. The filters ultimately depend on how much detail you have going for your design and how capable the filters can support such a wealth of hues.
It should also be apparent when dealing with more colors, but the upgrade of bits will be more taxing on your memory. While this may not be an issue for small images or those with low resolutions, this is crucial to be mindful of for more extensive and more color-dense images. Twice the colors mean apparent noticeable twice the memory.
There are also limitations on tools that can be used in 16-bit mode. One crucial tool hindered by this mode is the Art History Brush tool, as the program can’t handle such a powerful brush on such detailed images.
What it ultimately comes down to is what type of design you’re shooting for, and it doesn’t always need to be 16-bit. For example, if you know you’re only going to be using black and white with stark contrast, a depth of 1 bit can work well for this simplistic approach.
8-bit is perhaps better understood in Photoshop as the color mode of 256 uses. There are 256 gray values and 256 RGB color values for each channel, resulting in 16 million possible color choices.
Another way to look at images with 8 bits per channel is that they are sometimes recognized as 24-bit images given the three tracks. The math goes like this: 8 bits x 3 channels = 24 bits of data for each pixel.
The higher you go with the bits, the greater detail is possible with the many color choices. It’s why the more richly detailed images with 32 bits are more commonly referred to as high dynamic range images or HDR images for short.
Changing Bit Modes
So how do you turn these different modes on? Simply navigate through the menu to Image and then Mode. Under that submenu, you’ll find options for converting modes to 8-bit, 16-bit, or 32-bit. Keep in mind that making the shift may alter the appearance of your image or photo, so be mindful when converting.
Given the limitations within 16-bit, you may find yourself switching over to 8-bit if you need a specific filter or tool that just isn’t working in 16-bit. However, you’ll need to make sure that you back up your files be for converting and making altercations. This procedure should be standard when using Photoshop but double your efforts when it comes to bit conversation.
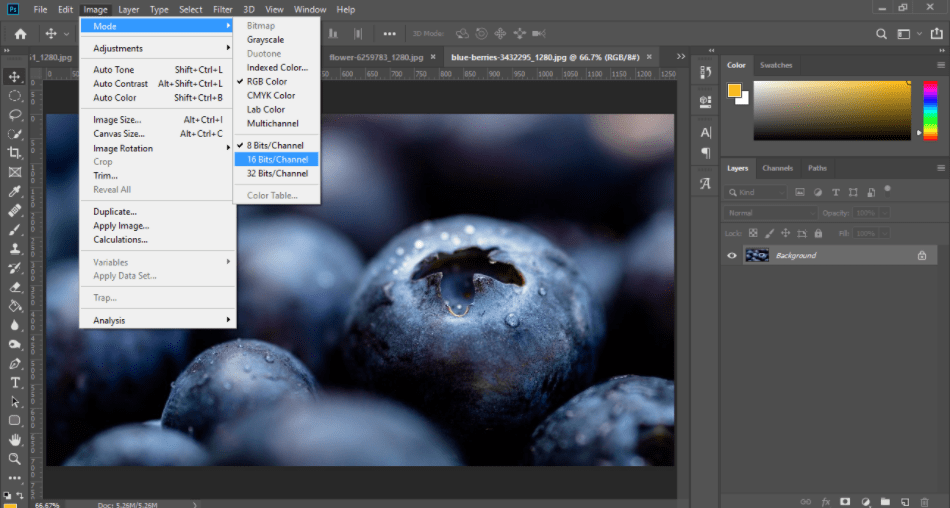
Bit recognition is also somewhat automatic depending on the types of images you bring into the program. If you were to bring in a small JPG, it’d most likely come in as 8 bit. If you get in a High Dynamic Range Image, it’ll recognize 32 bits.
Photoshop 8 bit vs 16 bit: When To Use Which Mode?
Despite Photoshop being able to recognize these detailed images, it’s still important to keep in mind the type of bit modes you’re working at so it doesn’t sneak up on you. As stated previously in this article, this relates to both details that would be gained or lost and various filters and adjustments that will change with conversions.
It’s essential to keep in mind bits even if you’re not working with images and just making rasterized art within the program. This can affect just how much detail you can display regarding both pen lines and colors pictured.
The choices when it comes to illustrations are a little easier to determine for most projects. If you’re crafting some retro video game graphics known for their smaller amounts of color, 8-bit is the obvious choice. For more detailed drawings of gradients and great attention, 16-bit seems like the best option.
The 32-bit mode, however, is not as highly recommended for illustration, considering how much memory it requires. Older computers may have difficulty handling the increase in colors coupled with tools that already need quite a bit of RAM for the most details. Tread carefully into 32-bit territory as crashing is likely.
Final Verdict
The big question about which color mode you should stick with ultimately depends on which bit count will suit your project. This is determined not just by the detail you expect out of the final product but also by the computer you’re working on as well.
8 bit is pretty much the default for the more specific projects and computers that are not as robust with RAM. It’s the leanest of the three modes to choose from and is capable of the most filters that can be applied to layers. There’s more that can be done when the color mode isn’t as dense.
16 bit will be of great benefit for photographers who find themselves working with high-quality photos. Clarity is the name of the game when it comes to rendering crisp and readable photography. For that purpose, 16 bit is the most capable mode to use in Photoshop.
32 bit should only be used in the most extreme of cases for the most powerful of projects. While 8 bit is capable of limited color combinations, speedy delivery, and numerous filters, 32 bit has far more colors, chunkier load times (depending on the machine). It holds more hindrances in its capable adjustments.
To keep things short and to the point, here’s a rough breakdown of each. 8-bit is your basic color mode for small projects and older machines. 16-bit is for higher quality for intermediate devices. 32-bit is ultra-quality for updated machines with the memory to handle the more increased flow of data.
There’s a lot to consider here, and it can seem like there’s a lot of info that has to be taken into account. Thankfully, the differences between 8-bit and 16-bit modes are not as vast, and you should have enough insight now to make an informed choice about what will work best for your photo or illustrative projects.
Frequently Asked Questions
The 8-bit mode of Photoshop operates on fewer color variations, being capable of 256 possible values for what you can compose with the colors. It is the mode most commonly used for RGB images and is the least taxing on computers for the limited range of color possibilities.
In most cases, the 8-bit mode should work just fine for your smaller projects. It is pretty much the default of Photoshop whenever you import an image. You should only use 16-bit when you need more detail or you’re dealing with higher quality photos you plan to edit with larger control over the colors.
8-bit Photoshop files can easily be converted to 16-bit with a simple switching of options. To accomplish this, simply navigate to Image > Mode > 16 Bits/Channel. Be aware, however, that when making this conversion not all of your options in terms of filters and changes will reflect with this change so it’s best to save a separate version.
The central difference between 8 bit and 16 bit in Photoshop is the way these different versions handle color. As one may expect, 8 bit has a limited range of color while 16 bit has an even vaster level of detail. However, 16 bit also increases file size, memory usage, and is limited in the different filters that can be used.

Mark McPherson has been working as a video editor and content writer for over ten years. His background started in animation and video editing before shifting into the realm of web development. He also branched out into content writing for various online publications. Mark is an expert in video editing, content writing, and 2D/3D animation.


